Non-pharmacological pain control during labor.
Scenario
- The couple have expressed a desire for non-pharmacological pain control during the labor. Describe the Gate-Control Theory of pain and discuss three methods of assisting the couple to achieve their goal of non-pharmacological pain control during the labor.
- The client calls the unit and tells a nurse that she thinks she is in labor. “I have had some pains for about 2 hours. Should my husband bring me to the hospital now?â Describe how a nurse should approach this situation.
- Write at least 3 questions a nurse would ask to elicit the appropriate information required to determine the course of action required. (Write out as if you were the nurse answering the phone)
- Based on the data collected during the telephone interview, the nurse determines that Mercy is in very early labor. Because she lives fairly close to the hospital, she is instructed to stay home until her labor progresses. Outline the instructions and recommendations (cite references and provide rationale) for care Mercy and her husband should be given for the nursing diagnosis: Readiness for enhanced knowledge of labor progression RT lack of exposure
- A week later, Mercy arrives to Labor and delivery at 39 weeks gestation. A nurse uses Leopoldâs maneuvers to assess the position of the baby in the uterus. A soft round mass is felt in the fundal region. A flat object is noted on the left and small objects are noted on the right of the uterus. A hard round mass is noted above the symphysis. The nurse would document which position consistent with these findings?
- The nurse notes on the labor record that the fetal heart tracing has the following: contraction frequency every 3 minutes, fundus palpates the same consistency as the forehead at the peak of contractions; fetal heart tones 140 bpm, early decelerations with each contraction and return to baseline, variability moderate. Explain what this assessment means.
- D.H. is admitted to labor and delivery for a labor induction with pitocin. Describe the procedure for pitocin induction.
a. What are the nursing responsibilities for safe administration of pitocin?
b. What are three potential complications? - D.H. complains of increasing headache, proteinuria is +3, and DTRâs are +3. Vital signs include Bp 154/94 mmHg, pulse 92. What is the primary concern based upon this assessment?
- The physician orders magnesium sulfate infusion 4 gram bolus over 30 minutes, then 2 gm per hour. The pharmacy sends up an IV bag of 1 liter Lactated Ringers with 40 mg magnesium sulfate for a secondary line. Describe the procedure for magnesium sulfate infusion.
a. What is the purpose for administering this medication?
b. At what rate will the bolus be administered in mL/hr?
c. Describe the adverse effects of magnesium sulfate administration.
d. What are the nursing responsibilities for safe administration of MgSO4? - D.H. is being induced for labor for the past 2 hours and her cervix is 5 cm/ 80%/ 0 station. Membranes are ruptured for one hour of light yellow, colored amniotic fluid.
Solution
Non-pharmacological pain control during labor.
- The couple have expressed a desire for non-pharmacological pain control during the labor. Describe the Gate-Control Theory of pain and discuss three methods of assisting the couple to achieve their goal of non-pharmacological pain control during the labor.
The Gate-Control Theory states that sensation of pain is transmitted along nerve pathways to the brain. There is a limited number of sensations that can travel along the pathways at a given time. Alternate activities can replace the pain sensation from traveling, which “closes the gate,” and reduces the amount of pain impulses traveling to the brain (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
One method that can help the couple is effleurage. This is cutaneous stimulation by lightly stroking the abdomen in rhythm with breathing during contractions. Another method is thermal simulation. This can be achieved by whirlpools, warm baths, or showers because they promote relaxation and comfort. The final method is mental stimulation. Playing music or imagery helps to take the focus away from the pain that the mother is feeling (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
2. The client calls the unit and tells a nurse that she thinks she is in labor. “I have had some pains for about 2 hours. Should my husband bring me to the hospital now?” Describe how a nurse should approach this situation.
The nurse would need to listen to the patient’s concerns. After listening to the patient’s concerns, the nurse should begin asking questions regarding the mother’s status and gestational history. This will allow the nurse to gain more information and be able to guide the mother on what she should do (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
By discussing when to go to the birthing facility with the pregnancy care provider before labor happens, women will have less anxiety and be more prepared when labor begins.
3. Write at least 3 questions a nurse would ask to elicit the appropriate information required to determine the course of action required. (Write out as if you were the nurse answering the phone)
Is this your first pregnancy?
How many weeks are you in this pregnancy?
Have you been told that this is pregnancy is high risk?
Are you having contractions? If so, how far apart are they? How long do they last? How long have you been contracting?
Are you leaking any fluids or bleeding?
How far do you live from the facility you chose to give birth at or the emergency room? (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
4. Based on the data collected during the telephone interview, the nurse determines that Mercy is in very early labor. Because she lives fairly close to the hospital, she is instructed to stay home until her labor progresses. Outline the instructions and recommendations (cite references and provide rationale) for care Mercy and her husband should be given for the nursing diagnosis: Readiness for enhanced knowledge of labor progression RT lack of exposure
Right now, we ask that you stay home. I recommend that you come to the labor and delivery if:
the contractions become stronger or start occurring closer together, where you are contracting every 5 minutes and they are lasting at least 60 seconds
your water breaks
the pain become very intense and unbearable
or, you start bleeding (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
Some things that you can do while at home to help with the pain are take a warm bath, listen to music to relax, have your husband give massage the area you are feeling the pain, and/or practice different breathing techniques.
A general rule of thumb for first-time pregnancy with no risk factors is to wait until contractions are 5 minutes apart, last 60 seconds, and are regular for at least an hour. She should go to the birthing center immediately if:
The membrane ruptures, or water breaks.
She is experiencing intense pain.
She is bleeding.
Recommendations for managing the pain stem from Gate-Control theory (Durham & Chapman, 2019)
5. A week later, Mercy arrives to Labor and delivery at 39 weeks gestation. A nurse uses Leopold’s maneuvers to assess the position of the baby in the uterus. A soft round mass is felt in the fundal region. A flat object is noted on the left and small objects are noted on the right of the uterus. A hard round mass is noted above the symphysis. The nurse would document which position consistent with these findings?
Left Occipital Anterior
The soft round mass felt in the fundal region is the baby’s butt. The flat object on the left is the baby’s back. The small objects on the right of the uterus are the baby’s hands and feet. The hard round mass found in the symphysis is the baby’s head (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
6.The nurse notes on the labor record that the fetal heart tracing has the following: contraction frequency every 3 minutes, fundus palpates the same consistency as the forehead at the peak of contractions; fetal heart tones 140 bpm, early decelerations with each contraction and return to baseline, variability moderate. Explain what this assessment means.
This is a category I tracing. They are strongly predictive of a well-oxygenated, nonacidotic fetus with a normal fetal acid-base balance. They may be followed in a routine manner and no action is required. Since the contractions are every 3 minutes and strong, the mother is most likely in Active phase of the first stage of labor (Durham & Chapman, 2019). D.H. is admitted to labor and delivery for a labor induction with pitocin. Describe the procedure for pitocin induction.
a) What are the nursing responsibilities for safe administration of pitocin?
Nursing responsibility during oxytocin infusion involves careful titration of the drug to the maternal-fetal response. The titration process includes decreasing the dosage rate or discontinuing the medication when contractions are too frequent, discontinuing the medication when fetal status is indeterminate or abnormal, and increasing the dosage rate when uterine activity and labor progress are inadequate (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
b) What are three potential complications?
Tachysystole leading to Category II (indeterminate) or Category III (abnormal) FHR pattern is the primary complication of oxytocin in labor.
Failed induction of labor: Failure to generate regular (e.g., every 3 minutes) contractions and cervical change after at least 24 hours of oxytocin administration, with artificial membrane rupture if feasible.
Water intoxication can occur with high concentrations of oxytocin with large quantities of hypotonic solutions, but usually only with prolonged administration with at least 40 mU/min (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
8. D.H. complains of increasing headache, proteinuria is +3, and DTR’s are +3. Vital signs include Bp 154/94 mmHg, pulse 92. What is the primary concern based upon this assessment?
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a hypertensive, multisystem disorder of pregnancy whose etiology remains unknown. Signs and symptoms include elevated blood pressure with a systolic pressure 140 mm Hg or greater and a diastolic pressure 90 mm Hg or greater, headache that will not go away with medication, increased deep tendon reflexes, and epigastric pain (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
9. The physician orders magnesium sulfate infusion 4 gram bolus over 30 minutes in a 100 ml bag, then 2 gm per hour. The pharmacy sends up an IV bag of 500 ml Lactated Ringers with 40 mg magnesium sulfate for a secondary line. Describe the procedure for magnesium sulfate infusion.
What is the purpose for administering this medication?
Magnesium sulfate, a central nervous system depressant, has been proven to help reduce seizure activity without documentation of long-term adverse effects to the woman and fetus (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- At what rate will the bolus be administered in mL/hr?
200 mL/hr
- Describe the adverse effects of magnesium sulfate administration.
Nausea
Flushing
Diaphoresis
Blurred vision
Lethargy
Hypocalcemia
Depressed reflexes
Respiratory
depression-arrest
Cardiac dysrhythmias
Decreased platelet aggregation
Circulatory collapse
Fetal heart rate decreased variability
Respiratory depression
Hypotonia (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- What are the nursing responsibilities for safe administration of MgSO4?
Assess vital signs before beginning infusion and every 5–15 minutes during loading dose, then every 30–60 minutes until the patient stabilizes. Frequency is then determined by the patient status.
Assess DTRs every 2 hours. Deep tendon reflexes can be elicited by striking the tendon of a partially stretched muscle briskly, using the flat or pointed surface of the reflex hammer
Monitor strict intake and output. Patients with oliguria or renal disease are at risk for toxic levels of magnesium.
Monitor serum magnesium levels
Monitor for signs and symptoms of magnesium toxicity (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- Review the stages of labor. What stage is D.H. in at this time based on the above information?
D.H is in the first stage of labor latent phase. Although her membranes are ruptured, she is only 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced and at 0 station (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- The obstetrician orders internal monitoring of the fetal heart rate and placement of an intrauterine pressure catheter to monitor contractions. Below is the tracing after 30 minutes of monitoring.
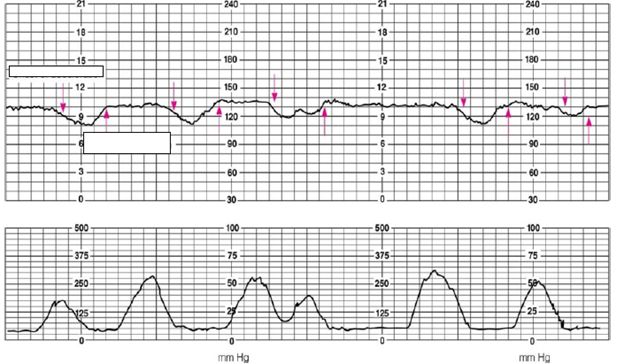
- What is the FHR?
130
- Describe the variability.
Moderate
- If there are any decelerations, what type is present?
Late
- What is the frequency of contractions?
Every 1-2 minutes
- What are the most appropriate nursing interventions at this time?
Assess FHR
Assess UCs for strength
Assess dilation
Provide calming support
Encourage the woman to breathe during contractions
Call Physician (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- If calling the physician was on the list of appropriate nursing interventions, Write out an SBAR to the physician at this time.
Hello Dr. Apple, this is Xzavia, SN in L&D. I am calling about D.H. G1P0. She was induced for labor for the past 2 hours and her cervix is 5 cm/ 80%/ 0 station. Membranes are ruptured for one hour light yellow, colored amniotic fluid. FHR 130, moderate variability, late decels, contractions are every 1-2 minutes. I recommend ordering medication for pain management
- D.H. elects to have epidural anesthesia to relieve the discomfort of labor. Following the initiation of epidural anesthesia, what is the nurse’s priority action?
- Checking for cervical dilation
- Placing the client in a supine position
- Checking the client’s blood pressure
- Obtaining a fetal heart rate
Nursing action before epidural is to assess the FHR to confirm a normal pattern (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
Priority Questions
- Several patients have just come into the obstetric triage unit. Which patient should the nurse assess first?
- . A 17-year-old gravida 1, para 0 (G1P0) woman at 40 weeks’ gestation with contractions every 6 minutes who is crying loudly and is surrounded by anxious family members
- . A 22-year-old G3P2 woman at 38 weeks’ gestation with contractions every 3 minutes who is requesting to go to the bathroom to have a bowel movement
- . A 32-year-old G4P3 woman at 27 weeks’ gestation who noted vaginal bleeding today after intercourse
- A 27-year-old G2P1 woman at 37 weeks’ gestation who experienced spontaneous rupture of mem- branes 30 minutes ago but feels no contractions
This patient may be in the second stage of labor. During the second stage, pain is caused by pelvic muscle distention and pressure on the perineum, cervix, urethra, and rectum. The feeling of having to make a bowel movement could be the woman bearing down (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- A 24-year-old gravida 2, para 1 woman is being admit- ted in active labor at 39 weeks’ gestation. What prenatal data would be most important for the nurse to address at this time?
- Hemoglobin level of 11 g/dL (110 g/L) at 28 weeks’ gestation
- . Positive result on test for group B streptococci at 36 weeks’ gestation
- . Urinary tract infection with Escherichia coli treated at 20 weeks’ gestation
- Elevated level on glucose screening test at 28 weeks’ gestation followed by normal 3-hour glucose tolerance test results at 29 weeks’ gestation
If a woman is GBS-positive at 35–37 weeks of gestation or GBS status unknown, she needs to be treated with antibiotics in labor to prevent neonatal transmission (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- The nurse in the labor and delivery unit is caring for a 25-year-old gravida 3, para 2 patient in active labor. The nurse has identified late fetal heart decelerations and decreased variability in the fetal heart rate and notified the health care provider (HCP) on call, who thinks that the pattern is acceptable. What would be the priority action at this time?
- Advise the patient that a different HCP will be called because the first HCP’s response was not adequate.
- Discuss the concerns with another labor and delivery nurse.
- Document the conversation with the HCP accurately, including the HCP’s interpretation and recommendation, and continue close observation of the fetal heart rate.
- Go up the chain of command and communicate the assessment of the fetal heart rate findings clearly to the next appropriate HCP.
This is a nonreassuring FHR, it will need to be reported (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- What would be the appropriate first nursing action when caring for a 20-year-old gravida 1, para 0 woman at 39 weeks’ gestation who is in active labor and for whom an assessment reveals mild variable fetal heart rate decelerations?
- Change the maternal position.
- Notify the provider.
- Prepare for delivery.
- Readjust the fetal monitor.
Variable heart decelerations are caused by compression on the umbilical cord (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- A 24-year-old gravida 1, para 0 patient, who is receiving oxytocin, is in labor at 41 weeks gestation. Which are appropriate nursing actions in the presence of late fetal heart rate decelerations? Select all that apply.
- . Discontinue the oxytocin.
- Decrease the maintenance IV fluid rate.
- Administer oxygen to the mother by mask.
- Place the woman in high Fowler position.
- Notify the health care provider
For Category II (indeterminate) or Category III (abnormal) FHR pattern, interventions include the following actions:
Discontinue oxytocin.
Change maternal position to left lateral position.
Initiate IV hydration of at least 500 mL lactated Ringer’s.
Administer O2 by nonrebreather mask at 10 L/min.
Consider terbutaline if no response.
Notify provider, observe, and reevaluate.
Notify the provider and request bedside evaluations for Category III abnormal FHR.
Assess emotional response of patient and support person to induction of labor. Provide information and reassurance as needed to alleviate feelings of failure.
Assess patient’s level of fear and provide information and reassurance. (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- A 22-year-old gravida 1, para 0 woman is being given an epidural anesthetic for pain control during labor and birth. Which are appropriate nursing actions when epidural anesthesia is used during labor? Select all that apply.
- Request the anesthesiologist to discontinue the epidural anesthetic when the patient’s cervix is completely dilated to allow the patient to sense the urge to push.
- Insert an indwelling catheter because the woman is likely to be unable to void.
- Encourage pushing efforts when the cervix is completely dilated in the absence of an urge to push.
- Encourage the patient to turn from side to side during the course of labor.
- Teach the patient that pain relief can be expected to last 1 to 2 hours.
Catherization is typically necessary for urinary retention after epidural and changing maternal position helps to progress labor (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- A 17-year-old gravida 1, para 0 woman at 40 weeks’ gestation is in labor. She has chosen natural childbirth with assistance from a doula. Her mother and her boy- friend are at the bedside. What nursing action can help the patient achieve her goal of an unmedicated labor and birth?
- Encourage the patient to stay in bed.
- Allow the patient’s support people to provide labor support and minimize nursing presence.
- Assess the effectiveness of the labor support team and offer suggestions as indicated.
- Offer pain medication on a regular basis so the patient knows it is available if desired.
Significant other(s) and/or a doula provide emotional support and physical comfort and aids in a beneficial form of care. Research has shown that support early in labor significantly relieves pain, improves outcomes, decreases interventions and complication rates, enhancing overall maternal satisfaction (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
- There are four patients on the busy labor and delivery unit undergoing induction of labor with oxytocin. The nurse supervisor for the unit is reviewing the patients. Which patient situation would require the supervising nurse to alert the bedside nurse to take immediate action?
- A patient with contractions every 10 minutes with a fetal heart rate of 150 beats/min.
- A patient with contractions every 1 1⁄2 minutes with a fetal heart rate of 140 beats/min.
- A patient with contractions every 5 minutes with a fetal heart rate of 130 beats/min who is moaning and crying.
- A patient with contractions every 6 minutes who is leaking clear amniotic fluid with a fetal heart rate of 150 beats/min.
This could indicate that the patient is in the transitional stage of labor (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
Ms. N arrives in the obstetrics triage area crying and accompanied by an agitated man who is speaking angrily to the client.
- Indicate the order in which the RN should take the following actions at this time.
- Apply a fetal monitor and measure vital signs.
- Obtain a thorough history from the client.
- Notify the HCP.
- Instruct the man to wait in the waiting area and notify security.
- Call a social worker for a consult.
___d__, ___a__, __c___, __b___, __e___
The nurse should look for the safety of the patient and the staff. Having the agitated man wait in the waiting area will ensure safety. Next would be monitoring the patient and the baby. After the HCP determines that the mother and baby are safe, the nurse can continue with a full assessment and notify social work for possible abuse if necessary (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
Ms. N relates that when she told her partner about the positive chlamydia test result, he became violent and began hit- ting her in the face and abdomen. Upon examination, Ms. N’s cervix is found to be 2 cm dilated and 50% effaced, she is contracting every 6 minutes, and she has a small amount of vaginal bleeding. Her ultrasound findings are normal and show no placenta previa. She is admitted to the hospital for treatment of preterm labor. The HCP has prescribed the fol- lowing medications: • Nifedipine 30 mg PO followed by 10 mg PO every 4 hours • Betamethasone 12 mg intramuscularly (IM) every 24 hours 2 doses
- What priority information would be important to give Ms. N about this treatment?
- Nifedipine and betamethasone work together to help stop preterm labor.
- Nifedipine is used to prevent neonatal heart problems after birth, and betamethasone is used to stop contractions.
- Betamethasone helps the infant’s lungs to mature and helps to prevent other neonatal complications if the infant is born preterm. Nifedipine used is to reduce the contractions.
- Nifedipine is used to treat chlamydia infection, and betamethasone is used to help the infant’s lungs mature.
Betamethasone is one antenatal steroid given to women to accelerate fetal lung maturity (Durham & Chapman, 2019).
Ms. N arrives at the hospital at 38 weeks’ gestation in active labor. Her membranes are intact. Her contractions are every 3 minutes. Her mother is at the bedside assisting her with breathing and relaxation. A vaginal examination reveals that the cervix is 5 cm dilated and 100% effaced, with the fetal head at 1 station. Her vital sign values are as follows: Blood pressure Heart rate Respiratory rate Temperature 140/90 mm Hg 88 beats/min 24 breaths/min 98.6°F (37°C) The fetal heart rate is 140 beats/min. There is average variability. Accelerations are present, and no decelerations are noted
11. Based on Ms. N’s vital sign measurements, what are the priority questions that the RN should ask? Select all that apply.
- Is she having headaches?
- Is she having pain with urination?
- Is she having epigastric pain?
- Is she experiencing visual changes?
- Has her water broken?
These are signs and symptoms of preeclampsia (Durham & Chapman, 2019). Durham, R & Chapman, L. (2019). Maternal-newborn nursing: The critical components of nursing care. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Company
Is this question part of your Assignment?
We can help
Our aim is to help you get A+ grades on your Coursework.
We handle assignments in a multiplicity of subject areas including Admission Essays, General Essays, Case Studies, Coursework, Dissertations, Editing, Research Papers, and Research proposals
Header Button Label: Get Started NowGet Started Header Button Label: View writing samplesView writing samples